XOS
Challenges for DataCenter:
Low resource utilization
Low resource utilization
Multi-core & many core
Challenges for Datacenter OS:
Bad Isolation
Gap between application and hardware
Scalability issue
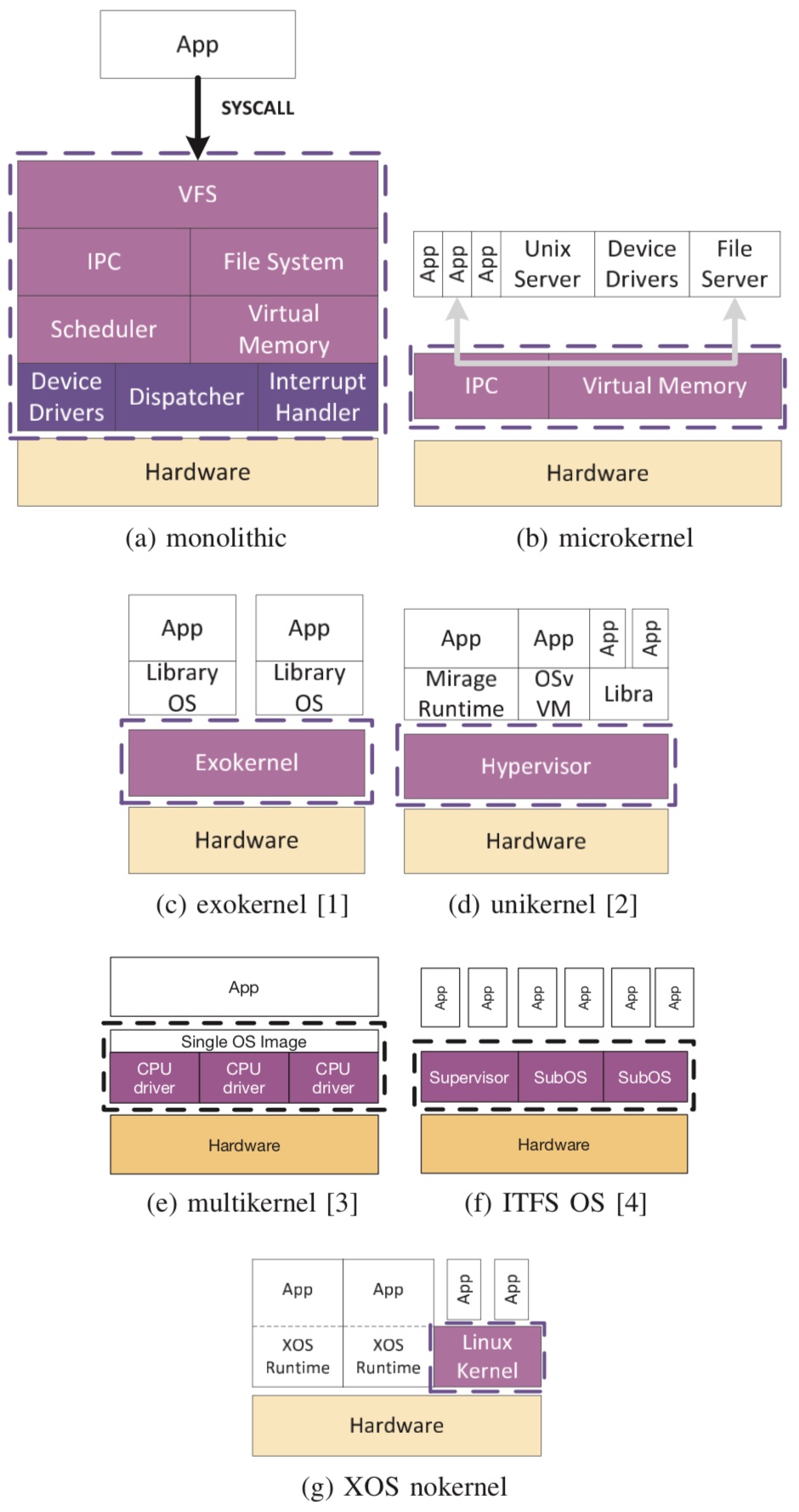
XOS is inspired by and built on much previous work in OSes to minimize the kernel, reduce competition for resources, and specialize functionalities for the needs of specific work- loads. Each of these design goals addresses some, but not all, of the requirements for DC workloads. Our application- defined OS model is made possible by hardware support for virtualizing CPU, memory, and I/O resources.
Application defined OS model:
General purpose: application define, bypass kernel
The design principles include:
Separating resource management
Application-defined Kernel Subsystems
Elastic Resource Partitioning
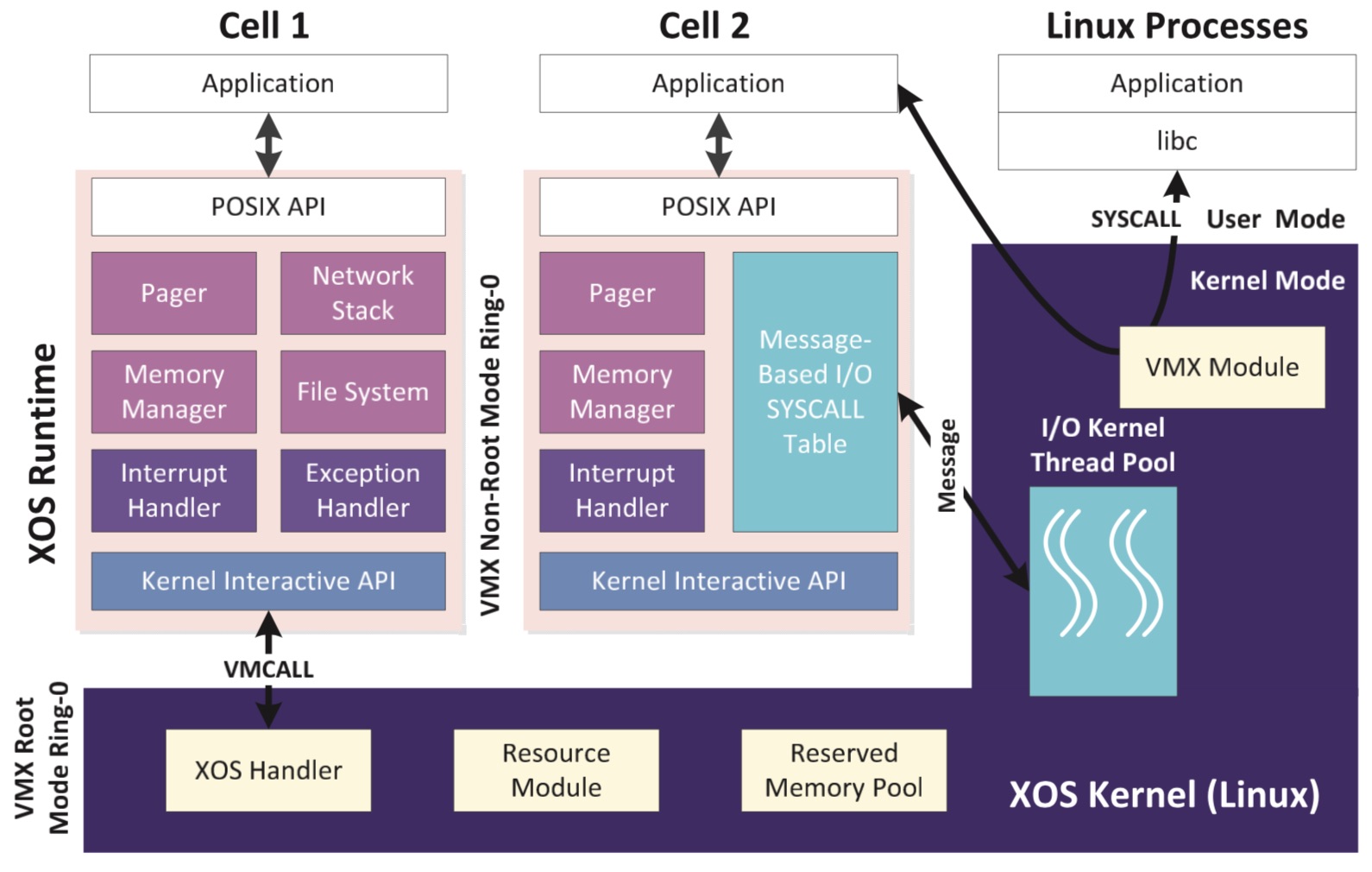
XOS: An Application-Defined Operating System for Datacenter Computing
Chen Zheng, Lei Wang, Sally A. McKee‡, Lixin Zhang, Hainan Ye and Jianfeng Zhan, 2018 IEEE International Conference on Big Data (IEEE Big Data 2018)
Abstract: Rapid growth of datacenter (DC) scale, urgency of cost control, increasing workload diversity, and huge software investment protection place unprecedented demands on the operating system (OS) efficiency, scalability, performance isolation, and backward-compatibility. The traditional OSes are not built to work with deep-hierarchy software stacks, large numbers of cores, tail latency guarantee, and increasingly rich variety of applications seen in modern DCs, and thus they struggle to meet the demands of such workloads.
This paper presents XOS, an application-defined OS for modern DC servers. Our design moves resource management out of the OS kernel, supports customizable kernel subsystems in user space, and enables elastic partitioning of hardware resources. Specifically, XOS leverages modern hardware support for virtualization to move resource management functionality out of the conventional kernel and into user space, which lets applications achieve near bare-metal performance. We implement XOS on top of Linux to provide backward compatibility. XOS speeds up a set of DC workloads by up to 1.6× over our baseline Linux on a 24-core server, and outperforms the state-of-the-art Dune by up to 3.3× in terms of virtual memory management. In addition, XOS demonstrates good scalability and strong performance isolation.